
Photo Courtesy: Henry Romero/Reuter
Mexico City CNN — Alejandro Gomez has been without proper running water for more than three months. Sometimes it comes on for an hour or two, but only a small trickle, barely enough to fill a couple of buckets. Then nothing for many days.
Gomez, who lives in Mexico City’s Tlalpan district, doesn’t have a big storage tank so can’t get water truck deliveries — there’s simply nowhere to store it. Instead, he and his family eke out what they can buy and store.
When they wash themselves, they capture the runoff to flush the toilet. It’s hard, he told CNN. “We need water, it’s essential for everything.”
Water shortages are not uncommon in this neighborhood, but this time feels different, Gomez said. “Right now, we are getting this hot weather. It’s even worse, things are more complicated.”
Mexico City, a sprawling metropolis of nearly 22 million people and one of the world’s biggest cities, is facing a severe water crisis as a tangle of problems — including geography, chaotic urban development, and leaky infrastructure — are compounded by the impacts of climate change.
Years of abnormally low rainfall, longer dry periods, and high temperatures have added stress to a water system already straining to cope with increased demand. Authorities have been forced to introduce significant restrictions on the water pumped from reservoirs.
“Several neighborhoods have suffered from a lack of water for weeks, and there are still four months left for the rains to start,” said Christian Domínguez Sarmiento, an atmospheric scientist at the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM).
Politicians are downplaying any sense of crisis, but some experts say the situation has now reached such critical levels that Mexico City could be barreling towards “day zero” in a matter of months — where the taps run dry for huge swaths of the city.
Historic lows
Densely populated Mexico City stretches out across a high-altitude lake bed, around 7,300 feet above sea level. It was built on clay-rich soil — into which it is now sinking — and is prone to earthquakes and highly vulnerable to climate change. It’s perhaps one of the last places anyone would choose to build a megacity today.
The Aztecs chose this spot to build their city of Tenochtitlan in 1325, when it was a series of lakes. They built on an island, expanding the city outwards, constructing networks of canals and bridges to work with the water.
But when the Spanish arrived in the early 16th century, they tore down much of the city, drained the lakebed, filled in canals and ripped out forests. They saw “water as an enemy to overcome for the city to thrive,” said Jose Alfredo Ramirez, an architect and co-director of Groundlab, a design and policy research organization.

Photo Courtesy : Cesar Rodriguez/Bloomberg/Getty Images
Their decision paved the way for many of Mexico City’s modern problems. Wetlands and rivers have been replaced with concrete and asphalt. In the rainy season, it floods. In the dry season, it’s parched.
Around 60% of Mexico City’s water comes from its underground aquifer, but this has been so over-extracted that the city is sinking at a frightening rate — around 20 inches a year, according to recent research. And the aquifer is not being replenished anywhere near fast enough. The rainwater rolls off the city’s hard, impermeable surfaces, rather than sinking into the ground.
The rest of the city’s water is pumped vast distances uphill from sources outside the city, in an incredibly inefficient process, during which around 40% of the water is lost through leaks.
The Cutzamala water system, a network of reservoirs, pumping stations, canals and tunnels, supplies about 25% of the water used by the Valley of Mexico, which includes Mexico City. But severe drought has taken its toll. Currently, at around 39% of capacity, it’s been languishing at a historic low.
“It’s almost half of the amount of water that we should have,” said Fabiola Sosa-Rodríguez, head of economic growth and environment at the Metropolitan Autonomous University in Mexico City.
In October, Conagua, the country’s national water commission, announced it would restrict water from Cutzamala by 8% “to ensure the supply of drinking water to the population given the severe drought.”
Just a few weeks later, officials significantly tightened restrictions, reducing the water supplied by the system by nearly 25%, blaming extreme weather conditions.
“Measures will have to be taken to be able to distribute the water that Cutzamala has over time, to ensure that it does not run out,” Germán Arturo Martínez Santoyo, the director general of Conagua, said in a statement at the time.

The exposed banks of the Villa Victoria Dam, part of the Cutzamala System, in Villa Victoria, Mexico on January 26, 2024.
Photo Courtesy :Raquel Cunha/Reuters
Around 60% of Mexico is experiencing moderate to exceptional drought, according to a February report. Nearly 90% of Mexico City is in severe drought — and it’s set to get worse with the start of the rainy season still months away.
“We are around the middle of the dry season with sustained temperature increases expected until April or May,” said June Garcia-Becerra, an assistant professor in engineering at the University of Northern British Columbia.
Natural climate variability heavily affects this part of Mexico. Three years of La Niña brought drought to the region, and then the arrival of El Niño last year helped deliver a painfully short rainy season that failed to replenish the reservoirs.
But the long-term trend of human-caused global warming hums in the background, fueling longer droughts and fiercer heat waves, as well as heavier rains when they do arrive.
“Climate change has made droughts increasingly severe due to the lack of water,” said UNAM’s Sarmiento. Added to this, high temperatures “have caused the water that is available in the Cutzamala system to evaporate,” she said.
Last summer saw brutal heat waves roil large parts of the country, which claimed at least 200 lives. These heat waves would have been “virtually impossible” without climate change, according to an analysis by scientists.
The climate impacts have collided with the growing pains of a fast-expanding city. As the population booms, experts say the centralized water system has not kept pace.
‘Day zero?’
The crisis has set up a fierce debate about whether the city will reach a “day zero,” where the Cutzamala system falls to such low levels that it will be unable to provide any water to the city’s residents.
Local media widely reported in early February that an official from a branch of Conagua said that without significant rain, “day zero” could arrive as early as June 26.
But authorities have since sought to assure residents there will be no day zero. In a press conference on February 14, Mexican President Andrés Manuel López Obrador said that work was underway to address the water problems. Mexico City’s mayor, Martí Batres Guadarrama, said in a recent press conference that reports of day zero were “fake news” spread by political opponents.
Conagua declined CNN’s interview requests and did not answer specific questions on the prospect of a day zero.
But many experts warn of a spiraling crisis. Mexico City could run out of water before the rainy season arrives if it carries on using it in the same way, Sosa-Rodríguez said. “It’s probable that we will face a day zero,” she added.
This doesn’t mean a complete collapse of the water system, she said, because the city isn’t dependent on just one source. It won’t be the same as when Cape Town in South Africa came perilously close to running totally dry in 2018 following a severe multi-year drought. “Some groups will still have water,” she said, “but most of the people won’t.”
Raúl Rodríguez Márquez, president of the non-profit Water Advisory Council, said he doesn’t believe the city will reach a day zero this year — but, he warned, it will if changes are not made.
“We are in a critical situation, and we could reach an extreme situation in the next few months,” he told CNN.
‘I don’t think anyone is prepared’
For nearly a decade, Sosa-Rodríguez said she has been warning officials of the danger of a day zero for Mexico City.
She said the solutions are clear: Better wastewater treatment would both increase water availability and decrease pollution, while rainwater harvesting systems could capture and treat the rain, and allow residents to reduce their reliance on the water network or water trucks by 30%.
Fixing leaks would make the system much more efficient and reduce the volume of water that has to be extracted from the aquifer. And nature-based solutions, such as restoring rivers and wetlands, would help provide and purify water, she said, with the added advantage of greening and cooling the city.
In a statement on its website, Conagua said it is undertaking a 3-year project to install, develop and improve water infrastructure to help the city cope with decreases in the Cutzamala system, including adding new wells and commissioning water treatment plants.
But in the meantime, tensions are rising as some residents are forced to cope with shortages, while others — often in the wealthier enclaves — remain mostly unaffected.
“There is a clear unequal access to water in the city and this is related to people’s income,” Sosa-Rodríguez said. While day zero might not be here yet for the whole of Mexico City, some neighborhoods have been grappling with it for years, she added.

Photo Courtesy : Henry Romero/Reuters
Amanda Martínez, another resident of the city’s Tlalpan district, said for people here, water shortages are nothing new. She and her family often have to pay more than $100 for a tank of water from one of the city’s water trucks. But it’s getting worse. Sometimes more than two weeks can go by without water and she fears what may be coming, she told CNN.
“I don’t think anyone is prepared.”
Neerain is proud to republish this blog for spreading awareness about situation of water, for our stake holders. Credit whatsoever goes to the Author.
This blog is published by:
CNN
We would like to spread this for the benefit of fellow Indians.
Author : Laura Paddison, Jack Guy and Fidel Gutiérrez
Published On: 25, February, 2024


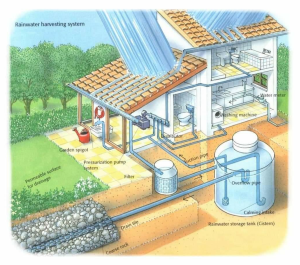


 Photo Courtesy : Deccan Chronicle
Photo Courtesy : Deccan Chronicle





 In Dhamdaha village of Purnia district of Bihar, yellowness is visible near the hand pump due to excess of iron. Whereas this hand pump has been installed by the government to provide iron free water. Photo: Pushya Mitra
In Dhamdaha village of Purnia district of Bihar, yellowness is visible near the hand pump due to excess of iron. Whereas this hand pump has been installed by the government to provide iron free water. Photo: Pushya Mitra The bench had gone into the details of the PIL and took note of the grave situation of water scarcity stated in the PIL in context to the urban areas of Pune district. The Bombay high court had taken note of the above information and had directed that a special committee be constituted separately for PMC and PCMC. And such committees shall attend to the complaints of the residents regarding water scarcity. The PMRDA was also directed to address the water problems faced by the residents coming under their jurisdiction.
The bench had gone into the details of the PIL and took note of the grave situation of water scarcity stated in the PIL in context to the urban areas of Pune district. The Bombay high court had taken note of the above information and had directed that a special committee be constituted separately for PMC and PCMC. And such committees shall attend to the complaints of the residents regarding water scarcity. The PMRDA was also directed to address the water problems faced by the residents coming under their jurisdiction. Photo: Ankur Paliwal
Photo: Ankur Paliwal